全球变暖背景下,极端天气气候事件日益频发,全球遭遇极端事件的风险加大。中国地理位置特殊,夏季极端高温、干旱事件频繁发生,复合高温干旱极端事件严重影响我国的经济、社会可持续发展,因此,为减轻极端事件风险,深入研究中国不同子区域复合高温干旱事件的变化特征及机理具有重要意义。近日,李惠心副教授(通讯作者)和其硕士研究生曾佳妮(第一作者)等探讨了中国夏季复合高温干旱事件的区域及次季节变化特征及机理,相关成果发表于期刊《Environmental Research Letters》。
本研究首先揭示了夏季不同月份复合高温干旱事件的分布特征,从趋势统计上看,全国大部分地区复合高温干旱事件呈显著增加趋势,而江淮地区夏季复合高温干旱事件的趋势始终不显著。夏季不同地区线性趋势有所不同:6月西部和南部沿海复合高温干旱事件的发生有显著增加趋势;7、8月中国北部和西部地区复合高温干旱事件的发生呈增加趋势。不同子区域的趋势表现出次季节差异,尤其在东部地区如东北、华北和华南地区。进一步对复合高温干旱事件发生频率的分析表明,20世纪90年代之前,其发生频率相对较低,而在随后的30年中,其发生频率有所增加,特别是在中国北部和西部地区。中国西南和西北东部是复合高温干旱事件发生频率最高的地区,而华南相对不受影响。在我国南方大部分地区6月复合高温干旱事件发生的频率高于7月和8月。最后就局地影响因子进行了讨论。中国东部地区复合高温干旱事件的发生受反气旋式环流异常的显著影响,对形成复合高温干旱事件所需的动力条件和水汽条件至关重要。
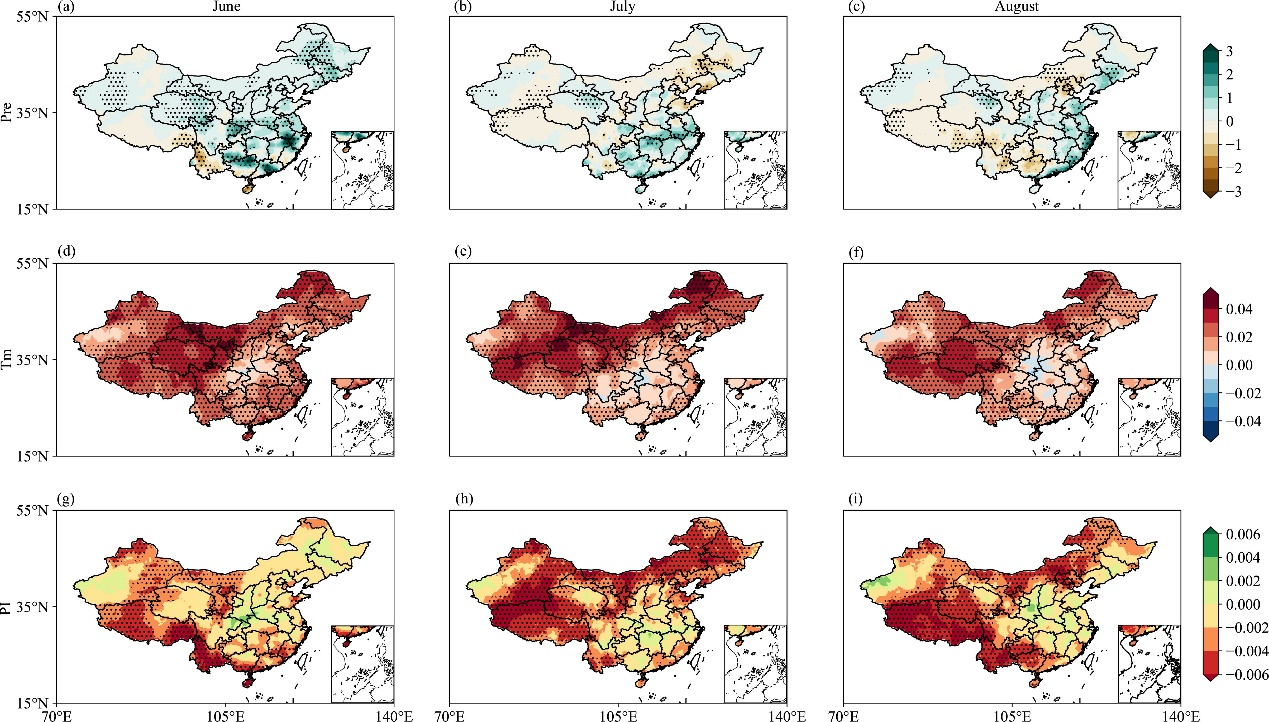
Fig. 1. The linear trend for (a, d, and g) precipitation, (b, e, and h) temperature, and (c, f, and i) the Probability Index (PI) during summertime (June, July, and August; JJA) for the period 1961–2022. Dotted regions indicate areas where the coefficient is significant at the 95% confidence level based on the Student’s t-test.
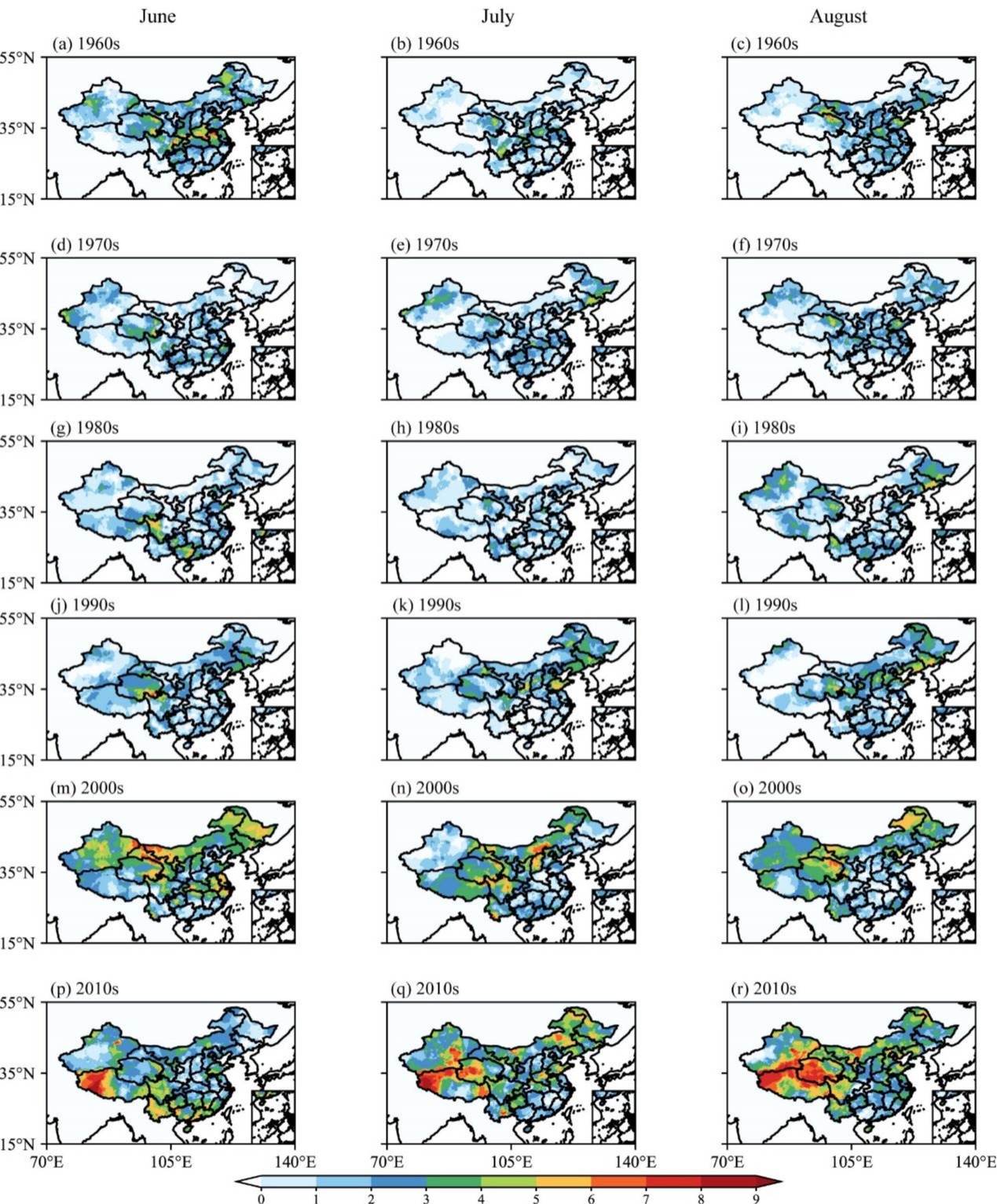
Fig. 2. Occurring frequency of severe compound heat wave and drought events (SCHDEs) in June, July, and August per decade over the previous 60 years: (a–c) the 1960s, (d–f) 1970s, (g–i) 1980s, (j–l) 1990s, (m–o) 2000s, and (p–r) 2010s (unit: number of SCHDEs/decade).
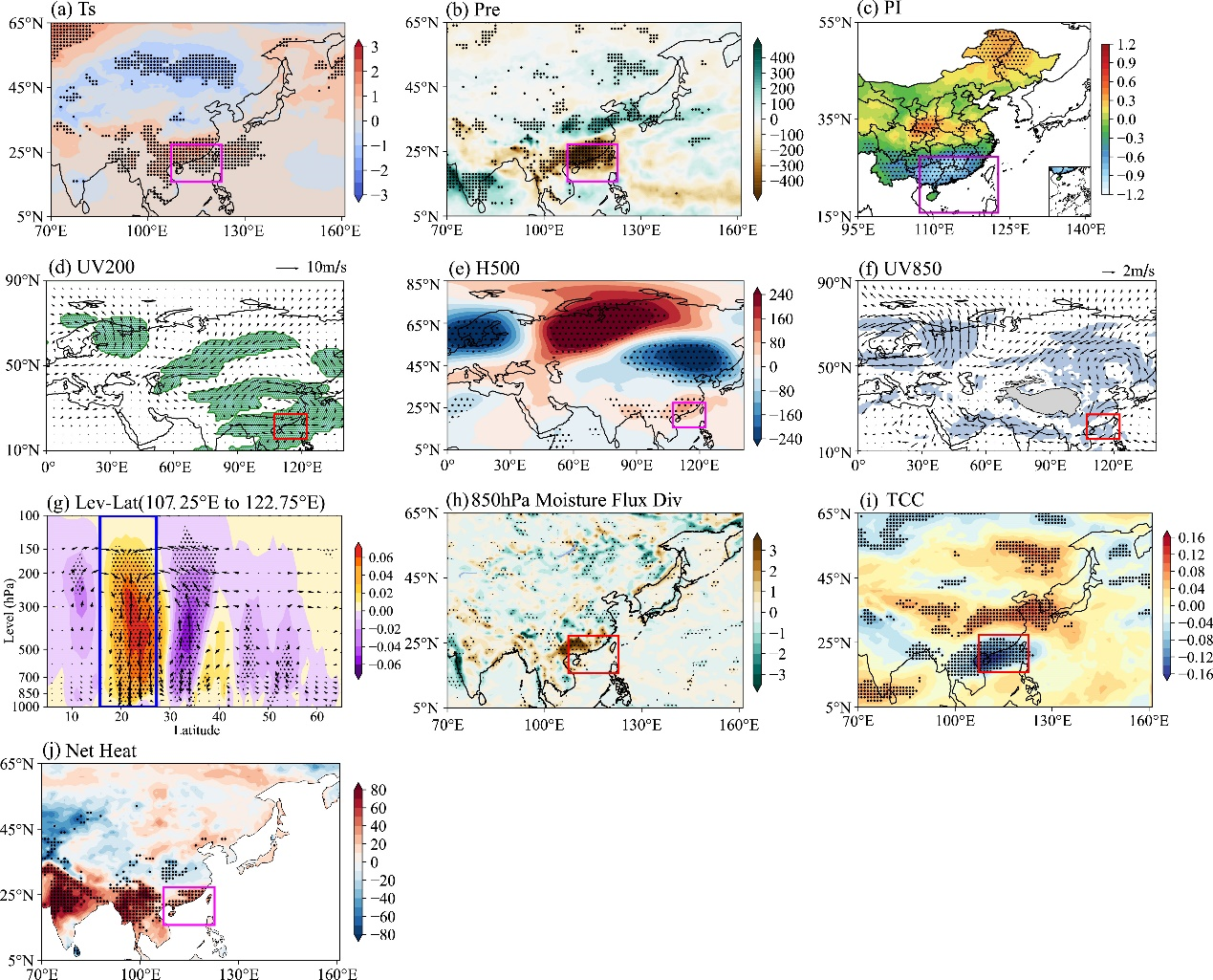
Fig. 3. Regression maps of the circulations in JJA over SC with regard to the PI during 1961–2022, including (a) 2-m air temperature (°C; shading), (b) precipitation (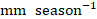 ; shading), (c) the PI, (d) 200-hPa wind (
; shading), (c) the PI, (d) 200-hPa wind (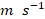 ; vectors), (e) 500-hPa geopotential height (gpm; shading), (f) 850-hPa wind (
; vectors), (e) 500-hPa geopotential height (gpm; shading), (f) 850-hPa wind (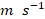 ; vectors), (g) vertical–horizontal cross section averaged along 107.25°–122.75°E for Omega (
; vectors), (g) vertical–horizontal cross section averaged along 107.25°–122.75°E for Omega (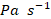 ;shading) and vertical wind (
;shading) and vertical wind (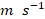 ; vectors), (h) 850-hPa moisture flux divergence (
; vectors), (h) 850-hPa moisture flux divergence (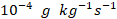 ; shading), (i) total cloud cover (%; shading), and (j) net surface heat flux (
; shading), (i) total cloud cover (%; shading), and (j) net surface heat flux (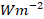 ; shading). Net surface heat flux anomalies are defined as positive downward. Regression coefficients based on the Student’s t-test that are significant at the 95% confidence level are indicated by stippling (200- and 850-hPa wind fields, and net surface heat are significant at the 90% confidence level). Here, the PI is multiplied by −1.
; shading). Net surface heat flux anomalies are defined as positive downward. Regression coefficients based on the Student’s t-test that are significant at the 95% confidence level are indicated by stippling (200- and 850-hPa wind fields, and net surface heat are significant at the 90% confidence level). Here, the PI is multiplied by −1.
相关文章:
Jiani Zeng, Huixin Li*, Bo Sun, Huopo Chen, Huijun Wang, Botao Zhou, Mingkeng Duan. 2024. Summertime compound heat wave and drought events in China: interregional and subseasonal characteristics, and the associated driving factors.Environmental Research Letters, DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/ad5576